Lecture Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy 4th Edition Answer Key: Unlocking the Cosmos is a comprehensive guide that empowers students to master the fundamentals of astronomy. This indispensable resource provides step-by-step solutions to the end-of-chapter questions, solidifying understanding and enhancing problem-solving skills.
With clear explanations and detailed illustrations, this answer key unravels the mysteries of the universe, covering topics such as the celestial sphere, coordinate systems, light and telescopes, planetary motion, stars, galaxies, and astrobiology. Dive into the vast expanse of the cosmos and discover the wonders that lie beyond our planet.
1. Introductory Astronomy
Course Overview

Introductory astronomy is a branch of science that explores the universe beyond Earth’s atmosphere. This course provides a comprehensive overview of the fundamental concepts and principles of astronomy, covering a wide range of topics from the celestial sphere to cosmology.
Key Concepts and Topics
- The celestial sphere and coordinate systems
- Light and telescopes
- Planetary motion and the solar system
- Stars and stellar evolution
- Galaxies and cosmology
- Astrobiology and the search for life
Course Structure and Organization
The course is organized into modules, each covering a specific topic. Modules include lectures, readings, assignments, and discussions. Students will engage with the material through a combination of online and in-person activities.
2. Celestial Sphere and Coordinate Systems
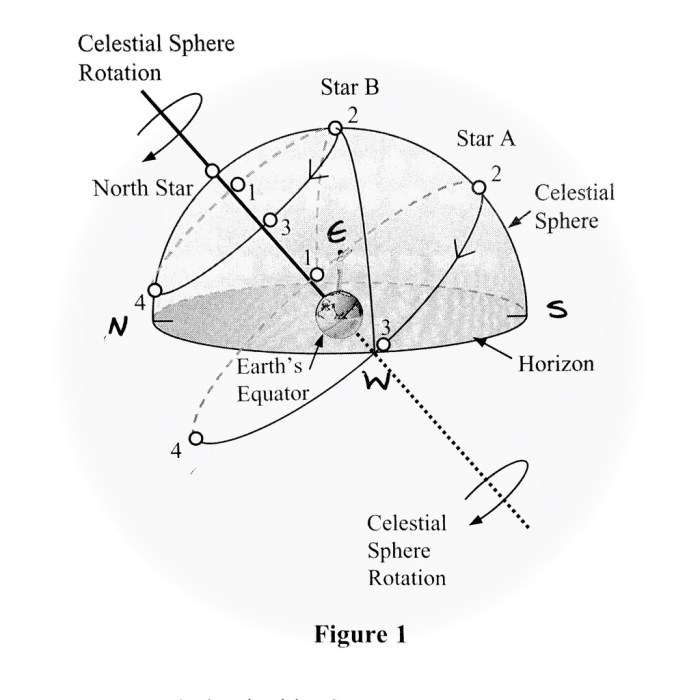
The celestial sphere is an imaginary sphere that surrounds Earth and contains all the celestial objects. It is used to describe the positions of celestial objects in the sky.
Coordinate Systems
- Horizontal coordinate system:Uses the horizon and zenith as reference points.
- Equatorial coordinate system:Uses the celestial equator and the vernal equinox as reference points.
- Ecliptic coordinate system:Uses the ecliptic (the Sun’s path across the sky) as a reference point.
Applications
Coordinate systems are used to locate celestial objects, track their movement, and determine their positions in the sky.
3. Light and Telescopes
Nature of Light
Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that travels in waves. It has properties such as wavelength, frequency, and intensity.
Telescopes, Lecture tutorials for introductory astronomy 4th edition answer key
- Refracting telescopes:Use lenses to focus light.
- Reflecting telescopes:Use mirrors to focus light.
Capabilities and Limitations
Telescopes allow us to observe faint objects, magnify distant objects, and collect more light. However, they also have limitations, such as atmospheric distortion and the diffraction limit.
4. Planetary Motion and the Solar System
Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion
- Law of Ellipses:Planets move in elliptical orbits around the Sun.
- Law of Equal Areas:A line connecting a planet to the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal time intervals.
- Law of Harmonies:The square of a planet’s orbital period is proportional to the cube of its average distance from the Sun.
Structure and Composition of the Solar System
The solar system consists of the Sun, eight planets, dwarf planets, moons, asteroids, and comets.
Characteristics of Planets, Moons, and Other Objects
Planets vary in size, mass, composition, and distance from the Sun. Moons are natural satellites that orbit planets. Other objects in the solar system include asteroids, comets, and meteoroids.
5. Stars and Stellar Evolution
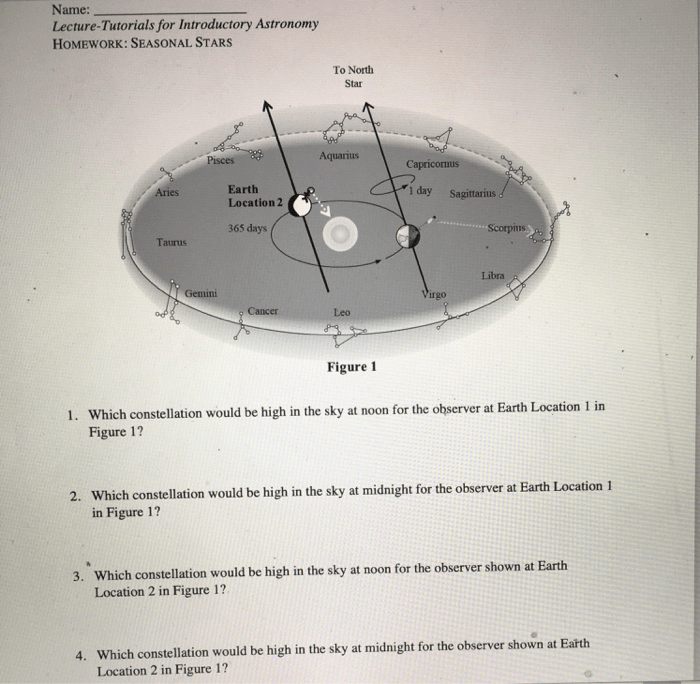
Properties and Characteristics of Stars
Stars are self-luminous celestial bodies that produce energy through nuclear fusion. They vary in size, mass, temperature, and luminosity.
Life Cycle of Stars
Stars evolve through different stages, from birth to death. The stages include the main sequence, red giant phase, and white dwarf, neutron star, or black hole stage.
Types of Stars
- O-type stars:Hot, blue, and massive
- B-type stars:Hot, blue, and less massive than O-type stars
- A-type stars:White and less massive than B-type stars
- F-type stars:Yellow-white and less massive than A-type stars
- G-type stars:Yellow, like our Sun
- K-type stars:Orange and less massive than G-type stars
- M-type stars:Red and the most common type of star
6. Galaxies and Cosmology
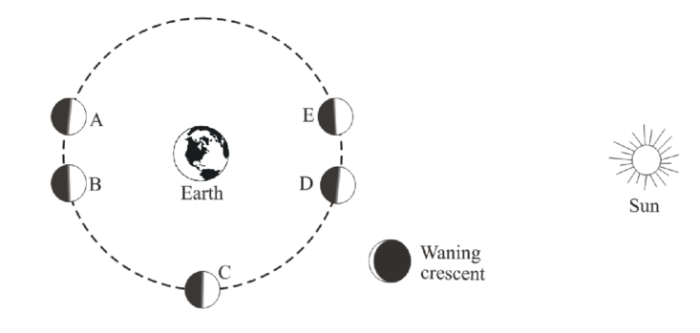
Structure and Properties of Galaxies
Galaxies are large collections of stars, gas, and dust held together by gravity. They come in different shapes and sizes, including spiral, elliptical, and irregular galaxies.
Types of Galaxies
- Spiral galaxies:Have a flat disk with spiral arms
- Elliptical galaxies:Have a smooth, round or elliptical shape
- Irregular galaxies:Have no regular shape
Cosmology
Cosmology is the study of the origin and evolution of the universe. It includes topics such as the Big Bang theory, dark matter, and dark energy.
7. Astrobiology and the Search for Life: Lecture Tutorials For Introductory Astronomy 4th Edition Answer Key
Concept of Astrobiology
Astrobiology is the study of the origin, evolution, and distribution of life in the universe. It explores the possibility of life beyond Earth.
Conditions Necessary for Life
Life as we know it requires certain conditions, including water, organic molecules, and a suitable temperature range.
Search for Extraterrestrial Life
Scientists are searching for extraterrestrial life using various methods, including radio telescopes, space probes, and the study of exoplanets.
FAQ Corner
Is the answer key suitable for students of all levels?
Yes, the answer key is designed to cater to students of all levels, from beginners to advanced learners.
Can I use the answer key to prepare for exams?
Absolutely, the answer key provides comprehensive solutions to end-of-chapter questions, making it an excellent resource for exam preparation.
Are the explanations in the answer key clear and concise?
Yes, the explanations are written in a clear and concise manner, ensuring that students can easily understand the concepts and problem-solving techniques.