Which of the following statements about distance is false sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. Prepare to embark on an intellectual journey that will challenge your understanding of distance, its properties, and its applications.
Distance, a fundamental concept in our physical world, has been extensively studied and applied across various disciplines. However, misconceptions and false statements about distance persist, hindering our accurate understanding of this crucial concept. This article aims to debunk these fallacies, providing a comprehensive exploration of distance and its true nature.
Understanding Distance
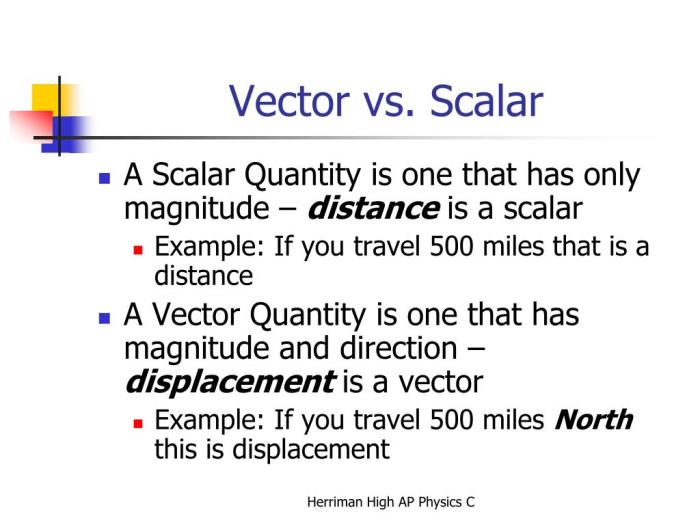
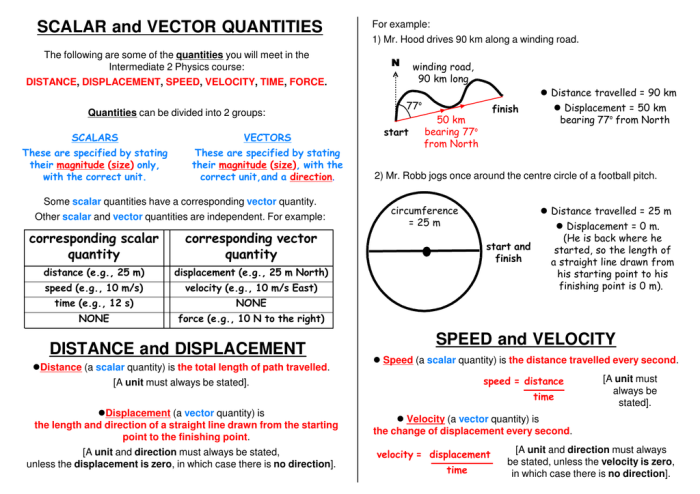
Distance is a fundamental concept in geometry and physics, representing the length or separation between two points in space. It is a scalar quantity, meaning it has only magnitude and no direction. The SI unit of distance is the meter (m), but other units such as kilometers (km), miles (mi), and feet (ft) are also commonly used.
Distance can be measured using various methods, including linear, aerial, and geodesic. Linear distance is the straight-line distance between two points, aerial distance is the distance measured along a curved path, and geodesic distance is the shortest distance between two points on a curved surface.
Properties of Distance, Which of the following statements about distance is false
- Non-negativity:Distance is always a non-negative quantity. The distance between two points cannot be negative.
- Symmetry:The distance between two points is the same regardless of the order in which they are considered. For example, the distance from point A to point B is the same as the distance from point B to point A.
- Triangle inequality:The distance between two points is less than or equal to the sum of the distances between each point and a third point. For example, if points A, B, and C are in that order, then the distance from A to C is less than or equal to the distance from A to B plus the distance from B to C.
Applications of Distance
- Navigation:Distance is used to determine the distance between two locations, such as the distance between two cities or the distance between a ship and a port.
- Surveying:Distance is used to measure the distance between points on a land surface, such as the distance between property boundaries or the distance between roads.
- Engineering:Distance is used to design and construct structures, such as the distance between the supports of a bridge or the distance between the floors of a building.
Common Misconceptions about Distance
- Distance is always the shortest path between two points.This is not always true. For example, the distance between two points on a curved surface, such as the Earth, is not the same as the straight-line distance between the two points.
- Distance can be negative.Distance is always a non-negative quantity. The distance between two points cannot be negative.
- Distance is the same in all directions.This is not always true. For example, the distance between two points on a curved surface, such as the Earth, is not the same in all directions.
User Queries: Which Of The Following Statements About Distance Is False
Is distance always a positive value?
Yes, distance is a non-negative quantity. It cannot be negative because it represents the length or separation between two points.
Can the distance between two points be zero?
Yes, the distance between two points can be zero if the points coincide or overlap.
Is the distance between two points always the same regardless of the path taken?
No, the distance between two points may vary depending on the path taken, especially if the path involves curves or non-straight lines.