The superficial muscles anterior view answer key provides a comprehensive understanding of the muscles visible on the front of the human body. This key is essential for medical professionals, students, and anyone interested in human anatomy.
The following guide will provide an overview of the superficial muscles of the anterior view, including their location, insertion, function, and clinical significance. Additionally, we will discuss the fascia associated with these muscles and how it helps organize them into groups.
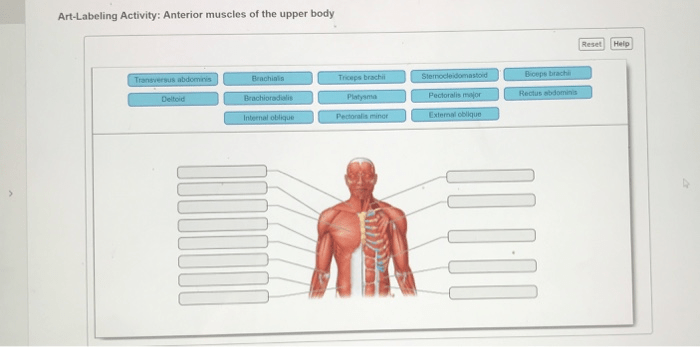
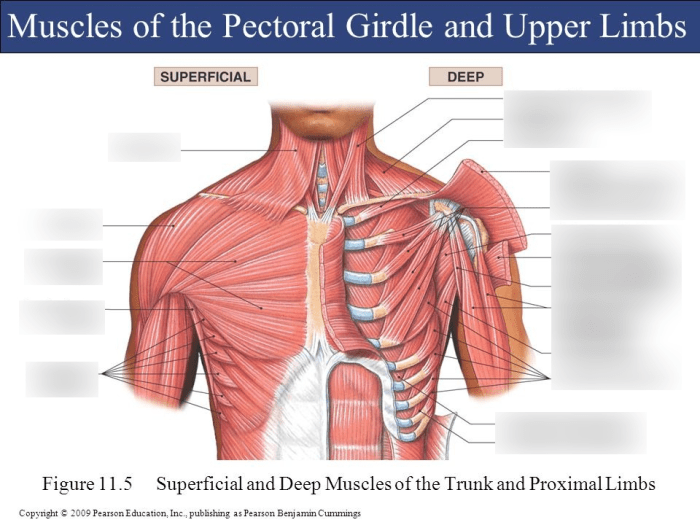
Superficial Muscles of the Anterior View: Superficial Muscles Anterior View Answer Key
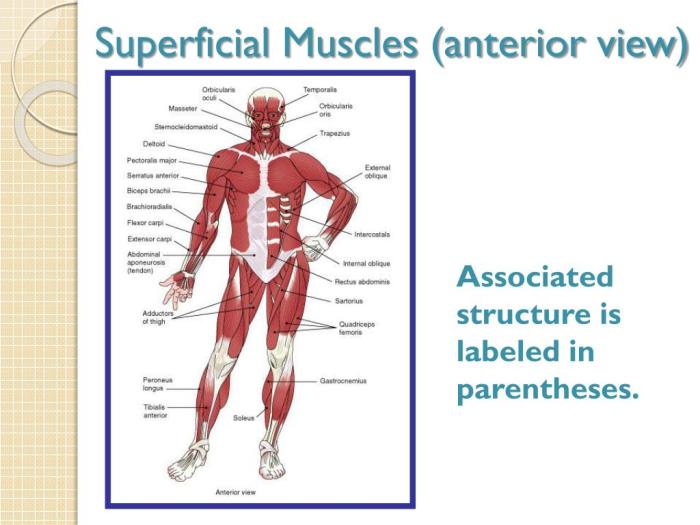
The superficial muscles of the anterior view are the muscles that lie directly beneath the skin and are visible on the front of the body. These muscles play an important role in movement, posture, and protection of the underlying organs.
The superficial muscles of the anterior view can be divided into three groups: the pectoralis group, the abdominal group, and the thigh group.
Fascia and Muscle Groups, Superficial muscles anterior view answer key
The superficial muscles of the anterior view are covered by a layer of fascia, which is a connective tissue that helps to organize the muscles into groups. The fascia also provides support and protection for the muscles.
The fascia associated with the superficial muscles of the anterior view can be divided into two layers: the superficial fascia and the deep fascia.
Blood Supply and Innervation
The superficial muscles of the anterior view are supplied by blood from the subclavian artery and the axillary artery. The nerves that innervate these muscles are the pectoral nerves, the intercostal nerves, and the femoral nerve.
- Pectoral nerves: Innervate the pectoralis major and pectoralis minor muscles.
- Intercostal nerves: Innervate the external oblique muscle and the internal oblique muscle.
- Femoral nerve: Innervates the quadriceps femoris muscle.
Clinical Applications
Understanding the superficial muscles of the anterior view is important for a variety of clinical applications, including physical examination, surgical procedures, and rehabilitation.
For example, knowledge of the superficial muscles of the anterior view can help clinicians to assess muscle injuries and dysfunctions. This information can be used to develop treatment plans and to monitor the progress of rehabilitation.
Imaging Techniques
The superficial muscles of the anterior view can be visualized using a variety of imaging techniques, including ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and computed tomography (CT).
Each of these techniques has its own advantages and disadvantages. Ultrasound is a relatively inexpensive and portable technique that can provide real-time images of the muscles. MRI is a more expensive technique that can provide detailed images of the muscles and their surrounding structures.
CT is a technique that can provide cross-sectional images of the muscles and their surrounding structures.
Helpful Answers
What are the superficial muscles of the anterior view?
The superficial muscles of the anterior view are the muscles that are visible on the front of the human body. These muscles include the pectoralis major, pectoralis minor, serratus anterior, rectus abdominis, and external oblique.
What is the function of the pectoralis major muscle?
The pectoralis major muscle is responsible for flexion, adduction, and medial rotation of the arm.
What is the clinical significance of understanding the superficial muscles of the anterior view?
Understanding the superficial muscles of the anterior view is important for physical examination, surgical procedures, and rehabilitation. For example, knowledge of these muscles is essential for assessing and treating muscle injuries and dysfunctions.