Dysrhythmia basic a relias answers – As Dysrhythmia Basic: A Reliable Source for Answers takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with authoritative knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of dysrhythmias, providing a thorough understanding of their definition, types, causes, and risk factors. It also explores the common signs and symptoms associated with dysrhythmias, emphasizing the importance of seeking medical attention when necessary.
Dysrhythmia Basic Overview
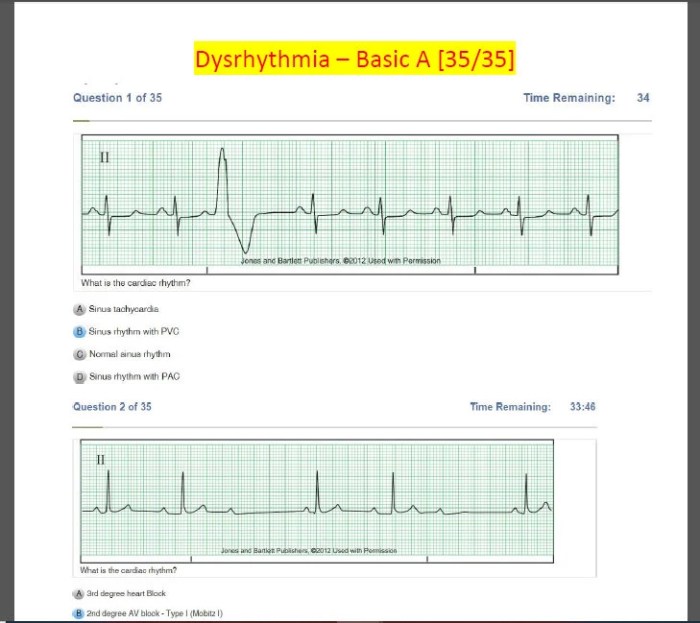
Dysrhythmias are abnormal heart rhythms that occur when the electrical impulses that coordinate heart contractions are disrupted. These disruptions can cause the heart to beat too fast, too slow, or irregularly.
There are various types of dysrhythmias, each with its own unique characteristics. Some common types include:
- Bradycardia: Heart rate is below 60 beats per minute (bpm).
- Tachycardia: Heart rate is above 100 bpm.
- Atrial fibrillation: Irregular heart rhythm originating in the atria.
- Ventricular tachycardia: Rapid heart rate originating in the ventricles.
Dysrhythmias can be caused by various factors, including underlying heart conditions, electrolyte imbalances, and certain medications. Risk factors include age, family history, and lifestyle choices such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Signs and Symptoms of Dysrhythmia
The signs and symptoms of dysrhythmias can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include:
- Palpitations (fluttering or racing heart)
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Shortness of breath
- Lightheadedness or dizziness
- Fatigue
- Syncope (fainting)
In some cases, dysrhythmias can be asymptomatic and detected only during routine medical examinations.
The severity of symptoms can range from mild to life-threatening. It is important to seek medical attention promptly if you experience any of these symptoms, especially if they are accompanied by chest pain or shortness of breath.
Dysrhythmias can significantly affect daily life and overall well-being. They can interfere with sleep, exercise tolerance, and work or school performance.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Dysrhythmia
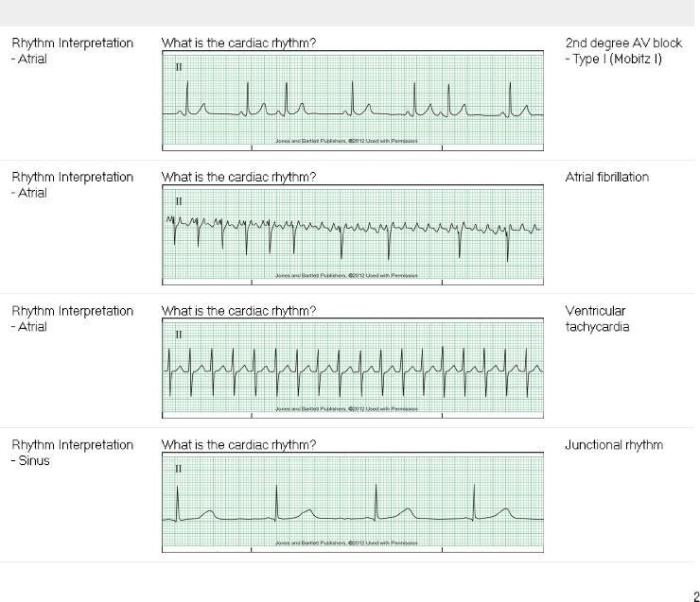
Diagnosing dysrhythmias typically involves a thorough medical history and physical examination. The doctor may order one or more of the following tests:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Records the electrical activity of the heart.
- Holter monitoring: Portable ECG that records the heart’s activity over 24 hours or more.
- Echocardiogram: Uses sound waves to create images of the heart.
- Electrophysiological study: Invasive procedure that evaluates the electrical system of the heart.
Treatment for dysrhythmias depends on the type and severity of the condition. Options include:
- Medications: Antiarrhythmic drugs can help regulate the heart’s rhythm.
- Lifestyle changes: Avoiding caffeine, alcohol, and smoking can help reduce the risk of dysrhythmias.
- Medical procedures: Catheter ablation or pacemaker implantation may be necessary for certain types of dysrhythmias.
Regular follow-up and monitoring are crucial after treatment to ensure the dysrhythmia is controlled and to detect any recurrence.
Prevention and Management of Dysrhythmia: Dysrhythmia Basic A Relias Answers

While some dysrhythmias cannot be prevented, there are steps you can take to reduce the risk of developing or recurring dysrhythmias:
- Manage underlying heart conditions.
- Control electrolyte imbalances.
- Avoid excessive alcohol and caffeine consumption.
- Quit smoking.
- Manage stress through exercise, yoga, or meditation.
Patient education and self-management are essential for managing dysrhythmias. Understanding your condition and its treatment plan will empower you to make informed decisions and actively participate in your care.
User Queries
What is the most common type of dysrhythmia?
Atrial fibrillation is the most common type of dysrhythmia, affecting millions of people worldwide.
What are the symptoms of dysrhythmia?
Symptoms of dysrhythmia can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition, but may include palpitations, chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness, and fainting.
How is dysrhythmia diagnosed?
Dysrhythmia is typically diagnosed using an electrocardiogram (ECG), which records the electrical activity of the heart.
What are the treatment options for dysrhythmia?
Treatment options for dysrhythmia vary depending on the type and severity of the condition, and may include medications, lifestyle changes, or medical procedures.