Exploring the intriguing realm of “matter from the mantle crossword,” this article delves into the captivating world of Earth’s geological makeup, offering a comprehensive examination of its composition, properties, origins, and diverse applications.
The mantle, a layer of Earth’s interior beneath the crust, plays a crucial role in shaping our planet’s surface and driving geological processes. By unraveling the secrets hidden within matter from the mantle, we gain a deeper understanding of Earth’s dynamic nature and its profound influence on life as we know it.
Matter from the Mantle
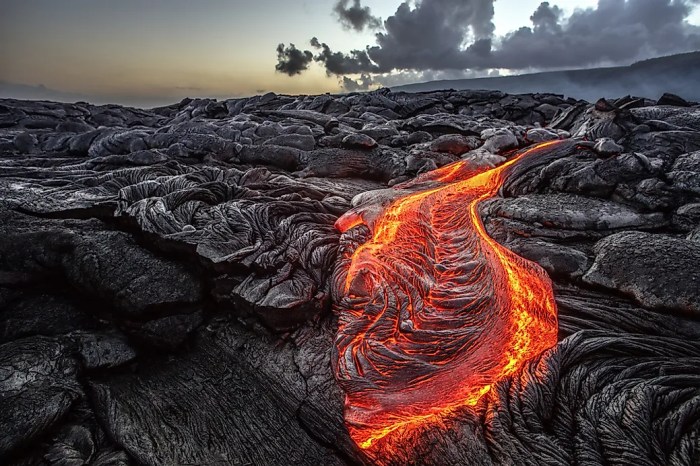

Matter from the mantle refers to the materials that constitute the Earth’s mantle, the layer beneath the crust and above the core. It is composed primarily of silicate rocks, with lesser amounts of iron, magnesium, calcium, and other elements.
Matter from the mantle plays a crucial role in the formation of the Earth’s crust through processes such as volcanic eruptions and plate tectonics. The movement of matter from the mantle to the surface provides essential nutrients and minerals for the formation of new rocks and the replenishment of existing ones.
Properties of Matter from the Mantle
Physical Properties
- High density (3.3-5.0 g/cm³)
- Solid or semi-solid state
- Extremely high temperatures (1,000-3,700°C)
- High pressure (10-20 GPa)
Chemical Properties
- Dominated by silicate minerals (e.g., olivine, pyroxene)
- Contains oxides of iron, magnesium, calcium, and other elements
- Low water content
- Contains volatile elements such as carbon dioxide and water
Thermal Properties
- High heat capacity
- Low thermal conductivity
- Undergoes phase changes due to temperature and pressure variations
Sources of Matter from the Mantle, Matter from the mantle crossword
Matter from the mantle is brought to the surface through various processes, including:
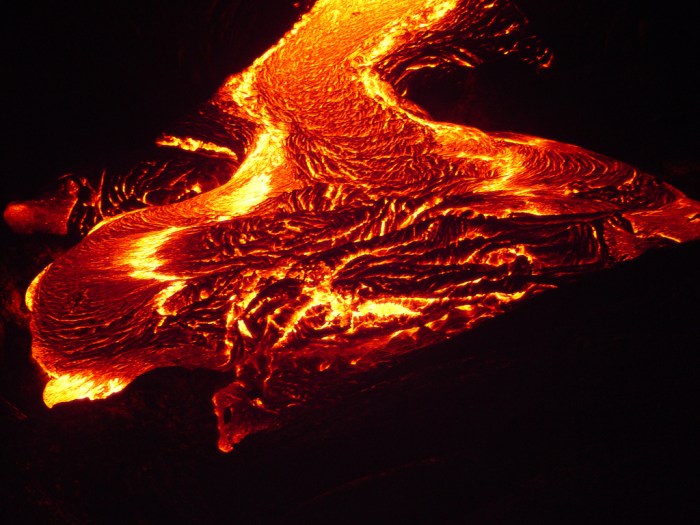
- Volcanic eruptions: Magma from the mantle rises through the crust and erupts onto the surface, releasing mantle material into the atmosphere and oceans.
- Plate tectonics: As tectonic plates move and interact, they can carry mantle material to the surface through processes such as subduction and accretion.
- Mantle plumes: Upwellings of hot mantle material can rise through the crust, forming volcanic hotspots and creating new landmasses.
Uses of Matter from the Mantle
Matter from the mantle has a wide range of industrial, agricultural, and environmental uses:
Industrial Uses
- Construction materials: Rocks and minerals from the mantle are used in the construction of buildings, roads, and other infrastructure.
- Mining: Valuable metals and minerals, such as gold, diamonds, and copper, are found in mantle-derived rocks.
- Geothermal energy: Heat from the mantle can be harnessed to generate electricity.
Agricultural Uses
- Soil fertility: Mantle-derived rocks provide essential nutrients for plant growth, such as potassium, phosphorus, and magnesium.
- Water resources: Groundwater and aquifers can be found in mantle-derived rocks.
Environmental Uses
- Carbon sequestration: Mantle-derived rocks can store carbon dioxide, reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Water filtration: Mantle-derived rocks can be used as filters to remove impurities from water.
FAQ Overview: Matter From The Mantle Crossword
What is matter from the mantle?
Matter from the mantle refers to the materials that make up the Earth’s mantle, a layer located beneath the crust and above the core.
How does matter from the mantle reach the surface?
Matter from the mantle can reach the surface through volcanic eruptions, where molten rock (magma) rises and solidifies to form new crustal material.
What are the industrial uses of matter from the mantle?
Matter from the mantle, particularly minerals and metals, is used in a wide range of industrial applications, including construction, manufacturing, and electronics.